Calcium Limit In Drinking Water. It enters drinking water supplies from natural deposits in the earth, or from agricultural and industrial practices.. When water is heated, calcium breaks down and precipitates out of the solution, forming scale.

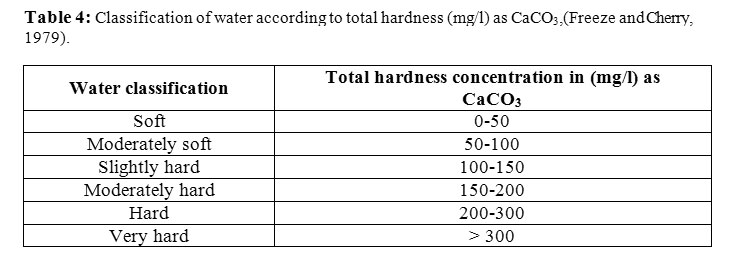
Water hardness (Calcium in water) is measured in grains per gallon (GPG) or milligrams per liter (mg/l, equivalent to parts per million, or ppm).
On one hand, you need calcium for strong bones and teeth.
Municipal Water Sources Tap water can be a significant source of both magnesium and calcium. It reveals the legal threshold limit of the substance on the amount allowed in public water systems under the Safe Drinking Water Act. Should I Be Concerned with Excess Calcium in my Drinking Water? Hard water is not a health risk, but a nuisance because of mineral buildup on fixtures and poor soap and/or detergent performance. When water is heated, calcium breaks down and precipitates out of the solution, forming scale. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety and are non-enforceable public health goals.
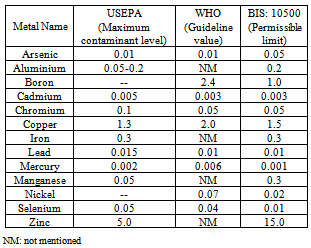
The standards set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for drinking water quality is denoted by Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs). MCLGs allow for a margin of safety and are non-enforceable public health goals. When water is heated, calcium breaks down and precipitates out of the solution, forming scale. Water is a great solvent for calcium and magnesium, so if the minerals are present in the soil around a water-supply well, hard water may be delivered to homes. S. are regulated by the Federal Clean Drinking Water act. These standards protect drinking water quality by limiting the levels of specific contaminants that can adversely affect public health and which are known or anticipated to occur in public.
Use a Brita filter to improve the taste of drinking water. Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) - The highest level of a contaminant that is allowed in drinking water. Maximum limits have not been established for calcium.