Permissible Limit Of Calcium In Drinking Water. On the other hand, too much calcium can result in more health problems than it solves. When water is heated, calcium breaks down and precipitates out of the solution, forming scale.
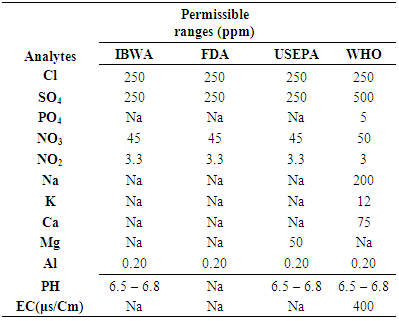
The standards set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for drinking water quality is denoted by Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs).
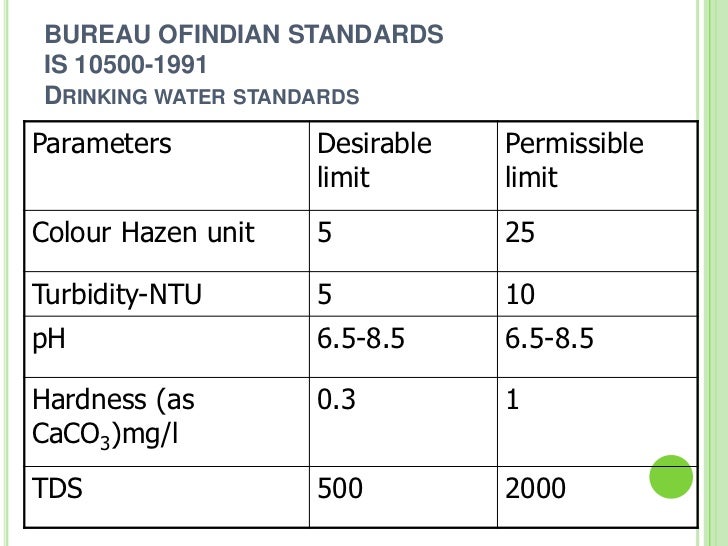
Hardness in water is most common problem we face in our daily life.
Maximum limits have not been established for calcium. On one hand, you need calcium for strong bones and teeth. When water comes in the form of rain it does not contain minerals, as it flows on the earth and filter. As far as the effects of calcium on human. found in water which can limit its use for irrigation. The bioavailability of calcium and magnesium is higher in water than in food. Health based guideline by the WHO.
On one hand, you need calcium for strong bones and teeth. The standard was adopted by the Bureau of Indian. A limit is placed on gross alpha-particle activity because it is impractical at the present time to identify all alpha- Primary drinking water standards. The bioavailability of calcium and magnesium is higher in water than in food. Normally found in fresh water/surface water/ground water. When water comes in the form of rain it does not contain minerals, as it flows on the earth and filter.
The bioavailability of calcium and magnesium is higher in water than in food. The hardness of water is determined by the milligrams of calcium carbonate per litre and is reported it in parts-per-million (ppm). Is calcium in drinking water a good or bad thing?